Nuclear Steam Power Plants
1. Pressurized Water Reactor (PWR)
Pressurized water reactors (PWRs) are nuclear power reactors that use ordinary water under high pressure as coolant and neutron moderator. The primary coolant loop is kept under high pressure to prevent the water from boiling. This puts strong requirements on the piping and pressure vessel and hence increases construction costs. PWRs are one of the most common types of reactors and are widely used all over the world. More than 230 of them are in use to generate electric power.
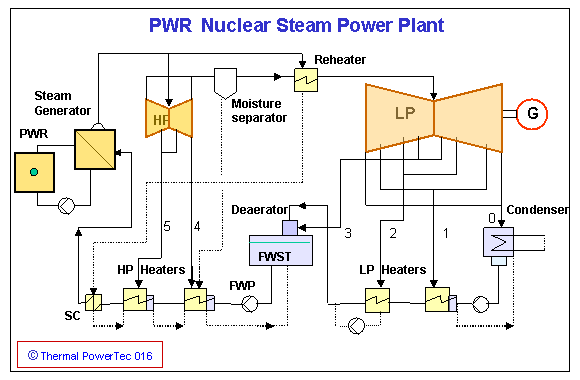
PWR has two coolant loops, so the water in the secondary loop is not contaminated by radioactive materials.
Ordinary water is used as primary coolant in a PWR and flows through the reactor at a temperature of roughly 315°C (600°F). The water remains liquid despite the high temperature due to the high pressure in the primary coolant loop (usually around 152 bar [2200 psig]). The primary coolant loop is used to heat water in a secondary circuit that becomes saturated steam (in most designs 62 bar [900 psi], 276°C [530°F]) for use in the steam turbine.
In a Secondary Cooling System (which include the Main Steam System and the Condensate-Feedwater Systems), cooler water is pumped from the Feedwater System and passes on the outside of those steam generator tubes, is heated and converted to steam. The steam then passes through the a Main Steam Line to the Turbine, which is connected to and turns the Generator. The steam from the Turbine condenses in a Condenser. The condensed water is then pumped by Condensate Pumps through Low Pressure Feedwater Heaters, then to the Feedwater Pumps, then to High Pressure Feedwater Heaters, then to the Steam Generators. The diagram above simplifies the process by showing the steam turbine, condenser, pumps, feedwater heaters, the steam generator, moisture separator and Reheater.
2. Boiling Water Reactor (BWR)The BWR typically allows bulk boiling of the water and is characterized by two-phase fluid flow (water and steam) in the upper part of the reactor core. The operating temperature of the reactor is approximately 300°C (570°F) producing steam at a pressure of about 70 bar (1000 psi). Current BWR reactors have electrical outputs of 570 to 1300 MWe.
The circulated water eventually is heated enough to convert to steam. Steam separators in the upper part of the reactor remove water from the steam. The steam then passes through the Main Steam Lines to the Turbine. The steam typically goes first to a smaller High Pressure (HP) Turbine, then passes to Moisture Separators, then to the 2 or 3 larger Low Pressure (LP) Turbines. There are 3 low pressure turbines, as is common for 1000 MWe plant. The turbines are connected to each other and to the Generator by a long shaft.
The steam, after passing through the turbines, then condenses in the Condenser, which is at a vacuum and is cooled by ocean, sea, lake, or river water. The condensed steam then is pumped to Low Pressure Feedwater Heaters. The water then passes to the Feedwater Pumps which in turn, pump the water to the reactor and start the cycle all over again.
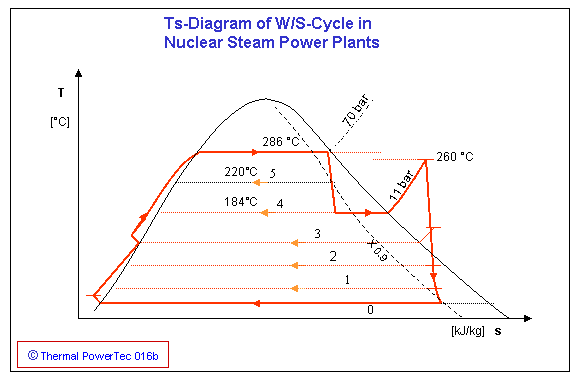
Nuclear power plants generally cannot reheat process steam due to safety requirements for isolation from the reactor core. This limits their thermodynamic efficiency to the order of 34–37%.


Tidak ada komentar:
Posting Komentar